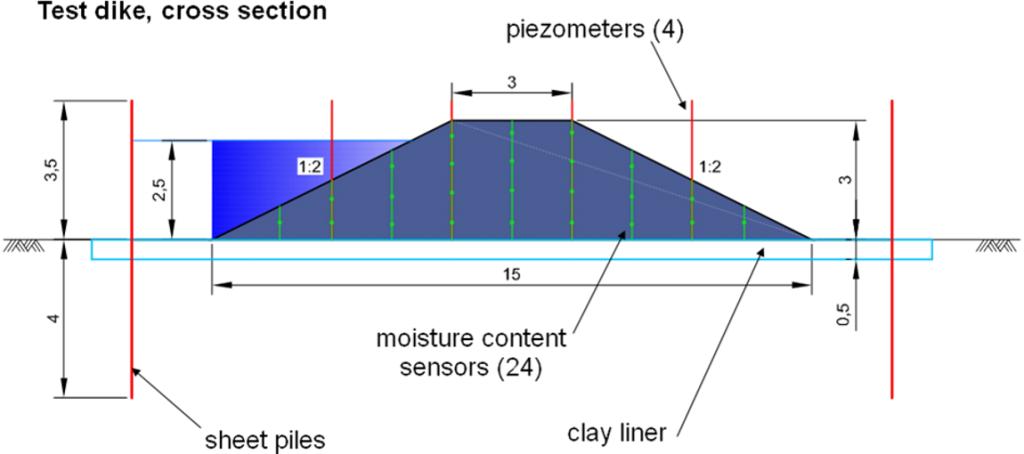
The full scale section of a dike with a dredged non-cohesive soil-coal ash compound body is planned to be investigated in Poland. The 4-meter wide test segment of the 24-meter long dike will be separated by sheet pile walls to obtain 2D plane conditions for seepage and overtopping with a controlled water level. The cross section of the test dike is shown in figure 1. Both slopes have inclination of 1:2 and the dike is 3.0 m high with a 3.0 m wide crest. To focus the attention on the seepage witin the dike, its bottom will be isolated from the permeable ground by 0,5 m thick clay liner. A high-water level of 2.5 m is planned to be maintained until the steady flow within the dike body is achieved. The instrumentation designed to control the development of percolation through the dike body consists of 4 piezometers and 24 moisture sensors. Additionally, sampling and laboratory testing of the physical and mechanical parameters of the applied sand-ash mixture are planned to be carried out during the test.
Currently, the details of the dike body structure are investigated. First, the proportions of the dredged sands, fly and fluidal ashes are studied in the laboratory to obtain the mixture with optimal properties for the dike. This is mainly focused on the seepage and mechanical properties of the mixture. Second, the technological aspects of the earth works during the construction of the dike are considered to make the designed structure feasible and easy to build.
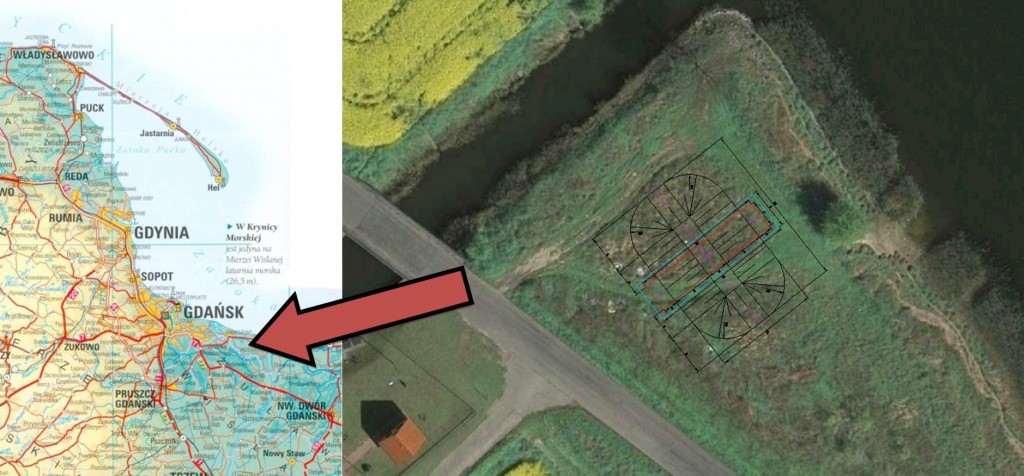
The test site will be located in Wiślinka/Trzcińsko on the bank of Vistula River ca. 20 km away from the City of Gdańsk. This location as well as arrangement of the test dike within the available area are shown in figure 2. The construction works are planned to start in the spring of 2012.
The ground under the test dike was extensively explored with the use of CPTU penetrometer. Under a shallow sandy crust, some fine grained soft deposits interbedded by sandy layers are probed. Due to good drainage conditions the consolidation of the soft depostis under additional loading is quite fast and it occurs almost entirely during the earth works. Additionally, appeared settlement are uniform what constitues a stable ground conditions.